Authors: Arunav Mallik Avi, Mustakim Billah
Platforms: Python (VS Code / PyCharm), Arduino Mega 2560
Keywords: Brain–Computer Interface (BCI), EEG, NeuroSky, Assistive Robotics, Human–Robot Interaction
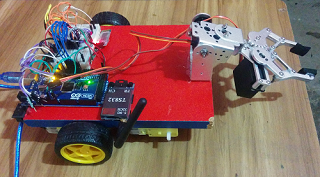
This project presents a low-cost Brain–Computer Interface (BCI) that enables real-time control of a 6-DOF robotic arm using EEG signals from the NeuroSky MindWave Mobile 2 headset. The system integrates a lightweight ThinkGear parser for EEG feature extraction (attention, meditation, blink strength, poor-signal level) and translates these into robotic commands via Arduino. A Tkinter-based graphical interface provides live EEG visualization, safety monitoring, and command logging. In addition, an Android Application can manually control the system through Google Speech Recogntion API. The prototype demonstrates the feasibility of using affordable EEG hardware for assistive robotics, paving the way for applications in rehabilitation, prosthetics, and human–robot interaction.
Human–robot interaction is a core area of modern robotics and healthcare engineering. Conventional robotic arm control relies on physical interfaces (joysticks, EMG sensors, or motion capture). However, patients with severe motor disabilities require more non-invasive and accessible interfaces. EEG-based BCIs represent a promising avenue, but most systems rely on expensive medical-grade hardware.
This work investigates whether a consumer-grade EEG headset (NeuroSky MindWave Mobile 2) can reliably control robotic manipulators and whether low-cost embedded controllers (Arduino) are sufficient for real-time actuation.
- MindWave Mobile 2 streams ThinkGear Protocol data
- Extracted features:
- Attention
- Meditation
- Blink Strength
- Poor Signal Level
Threshold-based mapping ensures reliability:
- Blink ≥ 60 → Toggle gripper (open/close)
- Attention ≥ 70 → Rotate base (joint 0)
- Meditation ≥ 70 → Lift shoulder (joint 1)
- Movement rate limited to 0.25s per command to prevent jitter
- Safety: commands ignored when poor signal > 50
- Arduino Mega receives ASCII commands:
S <joint> <delta>HOME
- Executes servo motion with predefined angle limits
- Emergency reset places arm into neutral home pose