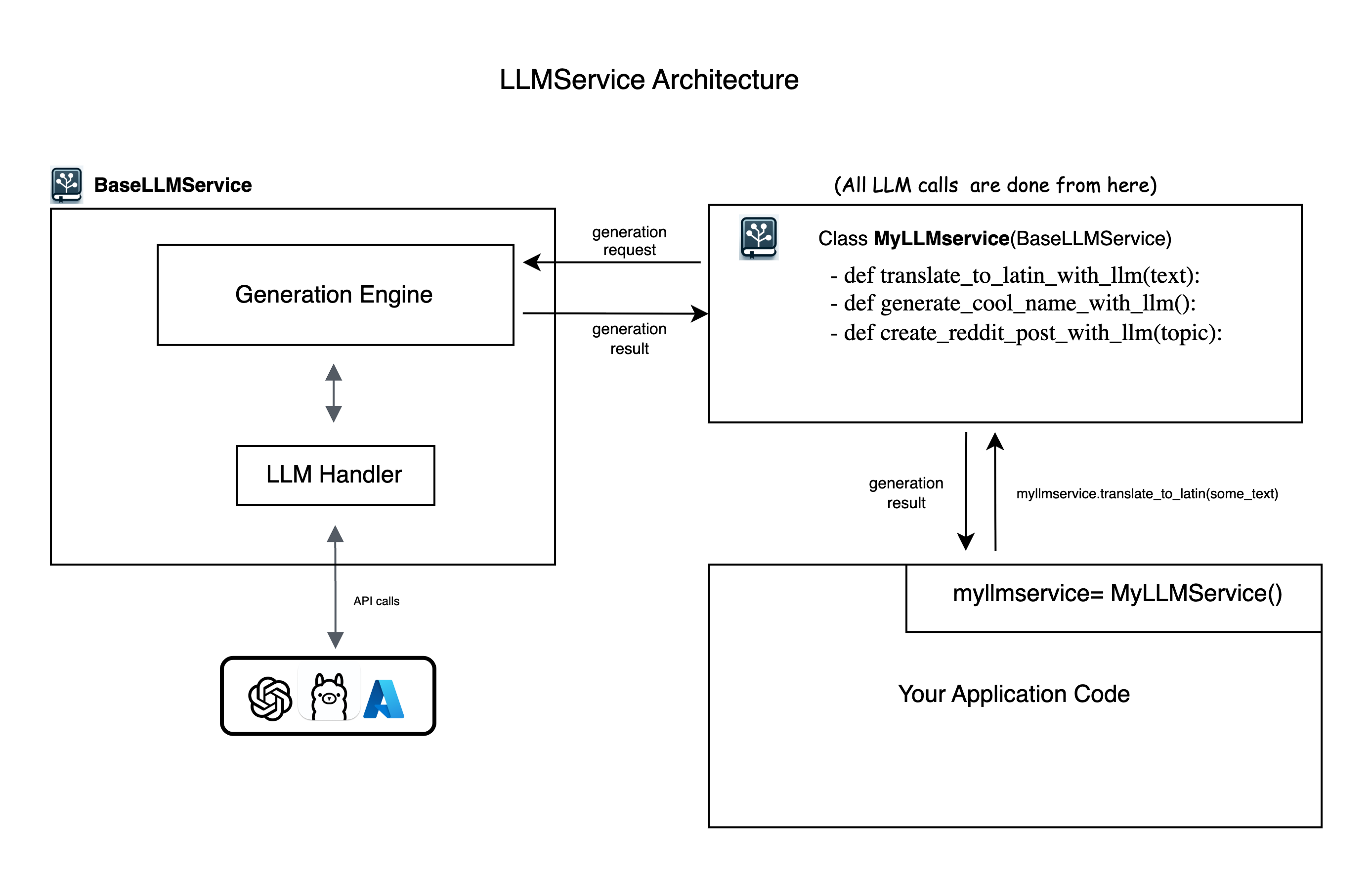
LLMService does one thing well - manage LLM invocations with production concerns (structured outputs, rate limits, costs, retries, extensive logging, scalable architecture).
A clean, production-ready service layer that centralizes prompts, invocations, and structured data extraction, ensuring rate-aware, maintainable, and scalable LLM logic in your application.
| Package |   |
Install LLMService via pip:
pip install llmservice- Installation
- What's New in v3.0
- What makes it unique?
- Main Features
- Architecture
- Usage
- Structured Outputs
- Async support
- Rate Limiting & Concurrency
- Cost Tracking
🚀 Structured Outputs with Pydantic - Direct extraction of typed data using Pydantic schemas, no more manual JSON parsing!
🎯 OpenAI Responses API - Full support for the latest OpenAI structured output features
❌ Pipeline Removal - Deprecated complex pipeline system in favor of clean, direct structured outputs
✨ Simplified API - Cleaner, more intuitive methods for common tasks
| Feature | LLMService | LangChain |
|---|---|---|
| Structured Outputs | Native Pydantic schema support with automatic validation and type safety via OpenAI's structured outputs API | Requires manual output parser setup and chaining |
| Result Handling | Returns a single GenerationResult dataclass encapsulating success/failure, rich metadata (tokens, cost, latency), and typed data |
Composes chains of tools and agents; success/failure handling is dispersed via callbacks and exceptions |
| Rate-Limit & Throughput Control | Built-in sliding-window RPM/TPM counters and an adjustable semaphore for concurrency, automatically pausing when you hit your API quota | Relies on external throttlers or underlying client logic; no native RPM/TPM management |
| Cost Monitoring | Automatic per-model token-level cost calculation and aggregated usage stats for real-time billing insights | No built-in cost monitoring—you must implement your own wrappers or middleware |
| Dependencies | Minimal footprint: only Tenacity, OpenAI client, and Pydantic | Broad ecosystem: agents, retrievers, vector stores, callback managers, and other heavy dependencies |
| Extensibility | Provides a clear BaseLLMService subclassing interface so you encapsulate each business operation and never call the engine directly |
You wire together chains or agents at call-site, mixing business logic with prompt orchestration |
LLMService delivers a well-structured alternative to more monolithic frameworks like LangChain.
"LangChain isn't a library, it's a collection of demos held together by duct tape, fstrings, and prayers."
-
Structured Outputs with Pydantic Define your expected output format as Pydantic models and get validated, typed responses directly.
-
Minimal Footprint & Low Coupling Designed for dependency injection—your application code never needs to know about LLM logic.
-
Result Monad Pattern Returns a
GenerationResultdataclass for every invocation, encapsulating success/failure status, raw and processed outputs, error details, retry information—giving you full control over custom workflows. -
Rate-Limit-Aware Asynchronous Requests Dynamically queue and scale workers based on real-time RPM/TPM metrics to maximize throughput without exceeding API quotas.
-
Transparent Cost & Usage Monitoring Automatically track input/output tokens and compute per-model cost, exposing detailed metadata with each response.
-
Automated Retry & Exponential Backoff Handle transient errors (rate limits, network hiccups) with configurable retries and exponential backoff powered by Tenacity.
-
Custom Exception Handling Provide clear, operation-specific fallbacks (e.g., insufficient quota, unsupported region) for graceful degradation.
LLMService provides an abstract BaseLLMService class to guide users in implementing their own service layers. It includes llm_handler which manages interactions with OpenAI's API and generation_engine which handles the process of prompt crafting, LLM invocation, and structured output processing.
-
Put your
OPENAI_API_KEYinside.envfile -
Install LLMService via pip:
pip install llmserviceCreate a new Python file (e.g., myllmservice.py) and extend the BaseLLMService class. All LLM logic for your business will be defined here as methods.
from llmservice import BaseLLMService, GenerationRequest
class MyLLMService(BaseLLMService):
def translate_to_latin(self, input_paragraph: str) -> GenerationResult:
my_prompt = f"translate this text to latin: {input_paragraph}"
generation_request = GenerationRequest(
user_prompt=my_prompt,
model="gpt-4o-mini",
operation_name="translate_to_latin"
)
# Execute the generation synchronously
generation_result = self.execute_generation(generation_request)
return generation_resultfrom pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from typing import List, Optional
class TranslationResult(BaseModel):
original_text: str = Field(description="The original text")
translated_text: str = Field(description="The translated text")
confidence: float = Field(ge=0, le=1, description="Translation confidence")
alternative_translations: Optional[List[str]] = Field(default=None)
class MyLLMService(BaseLLMService):
def translate_with_metadata(self, text: str, target_language: str) -> TranslationResult:
prompt = f"Translate '{text}' to {target_language}"
# Method 1: Using GenerationRequest with response_schema
request = GenerationRequest(
user_prompt=prompt,
response_schema=TranslationResult, # Pydantic schema
model="gpt-4o-mini",
operation_name="structured_translation"
)
result = self.execute_generation(request)
if result.success:
# Content is already parsed and validated
import json
return TranslationResult(**json.loads(result.content))
else:
# Handle error
raise Exception(f"Translation failed: {result.error_message}")# in your app code anywhere you need to run LLM logic
from myllmservice import MyLLMService
if __name__ == '__main__':
myllmservice = MyLLMService()
# Simple text generation
result = myllmservice.translate_to_latin("Hello, how are you?")
print(result.content) # "Salve, quomodo vales?"
# Structured output
translation = myllmservice.translate_with_metadata(
text="Hello world",
target_language="Spanish"
)
print(translation.translated_text) # "Hola mundo"
print(translation.confidence) # 0.95Below is the structure of the GenerationResult dataclass. While the .content field provides the direct LLM response, advanced applications will benefit from leveraging the full set of metadata.
@dataclass
class GenerationResult:
success: bool
trace_id: str
request_id: Optional[Union[str, int]] = None
content: Optional[Any] = None # For structured outputs, this is JSON string
raw_content: Optional[str] = None # Store initial LLM output
raw_response: Optional[Any] = None # Complete response object
operation_name: Optional[str] = None
usage: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict)
elapsed_time: Optional[float] = None
error_message: Optional[str] = None
model: Optional[str] = None
response_type: Optional[str] = None
response_id: Optional[str] = None # For CoT chaining
# Rate limit tracking
rpm_at_the_beginning: Optional[int] = None
rpm_at_the_end: Optional[int] = None
tpm_at_the_beginning: Optional[int] = None
tpm_at_the_end: Optional[int] = None
# ... and more metadata fields# Success checking
if not res.success:
print("LLM call failed:", res.error_message)
# Token and cost breakdown
print("Input tokens:", res.usage["input_tokens"])
print("Output tokens:", res.usage["output_tokens"])
print("Total cost (USD):", res.usage["total_cost"])
# Latency info
print("LLM round-trip (ms):", res.elapsed_time * 1000)
# Rate-limit stats
print("RPM at start:", res.rpm_at_the_beginning)
print("RPM at end:", res.rpm_at_the_end)LLMService provides multiple ways to work with structured outputs using Pydantic schemas:
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
class ProductInfo(BaseModel):
name: str = Field(description="Product name")
price: float = Field(gt=0, description="Price in USD")
in_stock: bool = Field(description="Availability")
request = GenerationRequest(
user_prompt="Extract product info from: 'iPhone 15 Pro - $999, available now'",
response_schema=ProductInfo,
model="gpt-4o-mini"
)
result = myllmservice.execute_generation(request)
# result.content contains validated JSON matching ProductInfo schemafrom llmservice import GenerationEngine
engine = GenerationEngine(model_name="gpt-4o-mini")
# Direct structured generation
product = engine.generate_structured(
prompt="Extract product info from: 'MacBook Pro M3 - $1999, in stock'",
schema=ProductInfo,
system="You are a product data extractor"
)
# Returns parsed ProductInfo instance directly
print(f"Product: {product.name}, Price: ${product.price}")# Process already generated content
raw_llm_output = "The product is iPhone 15 at $999 and it's available"
product = engine.process_with_schema(
content=raw_llm_output,
schema=ProductInfo,
system="Extract product information"
)class Address(BaseModel):
street: str
city: str
country: str
class Customer(BaseModel):
name: str
email: str
addresses: List[Address]
preferred_contact: Literal["email", "phone", "mail"]
# Works with nested schemas automatically
customer = engine.generate_structured(
prompt="Create a customer record for John Doe...",
schema=Customer
)LLMService includes first-class asynchronous methods with built-in rate and concurrency controls:
class MyLLMService(BaseLLMService):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__(
default_model_name="gpt-4o-mini",
max_rpm=120, # Max requests per minute
max_tpm=10_000, # Max tokens per minute
max_concurrent_requests=50 # Concurrent request limit
)
async def translate_async(self, text: str, target_lang: str) -> GenerationResult:
request = GenerationRequest(
user_prompt=f"Translate to {target_lang}: {text}",
model="gpt-4o-mini",
operation_name="async_translation"
)
return await self.execute_generation_async(request)
# Usage
import asyncio
async def translate_batch(texts: List[str]):
myllmservice = MyLLMService()
tasks = [myllmservice.translate_async(text, "Spanish") for text in texts]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
return resultsLLMService provides sophisticated rate limiting with sliding window tracking:
myllmservice = MyLLMService()
# Set rate limits
myllmservice.set_rate_limits(max_rpm=100, max_tpm=20_000)
myllmservice.set_concurrency(max_concurrent_requests=25)
# Monitor current rates
snapshot = myllmservice.metrics.snapshot()
print(f"Current RPM: {snapshot.rpm}")
print(f"Current TPM: {snapshot.tpm}")
print(f"Total cost: ${snapshot.cost:.4f}")Track costs at operation level:
# Get usage statistics per operation
stats = myllmservice.usage_stats.operation_usage
for operation, usage in stats.items():
print(f"{operation}:")
print(f" Total tokens: {usage['total_tokens']}")
print(f" Total cost: ${usage['total_cost']:.6f}")
# Get total usage
total = myllmservice.usage_stats.total_usage
print(f"Session total: ${total['total_cost']:.6f}")Check out the examples/ directory for complete working examples:
- capital_finder: Basic text generation and structured data extraction
- SQL_code_generator: Generate SQL from natural language with validation
- translator: Multi-language translation with async batch processing
MIT
Contributions are welcome! Please feel free to submit a Pull Request.