Mojo is a high-performance, multithreaded web crawler tailored for creating high-quality datasets for Large Language Models (LLMs) and AI training. Written in modern C++20 with coroutines, it rapidly fetches entire websites and converts them into clean, structured Markdown, making it the ideal tool for building knowledge bases and RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) pipelines.
You can download the latest pre-compiled binaries from the Releases page.
For maximum compatibility, we recommend using the official packages which automatically handle dependencies:
Debian / Ubuntu / Kali / Mint:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ./mojo-0.1.0-debian.debCentOS / RHEL / Fedora:
sudo yum install epel-release
sudo yum install ./mojo-0.1.0-rhel.rpm- Download
mojo-macos-arm(M1/M2/M3) ormojo-macos-intel. - Move it to your bin folder and give it execution permissions:
chmod +x mojo-macos-arm
sudo mv mojo-macos-arm /usr/local/bin/mojo- Make sure to grant privileges to the binary via security settings, since it is not signed.
- Download
mojo-windows-x64.exe. - Run it from your terminal (CMD/Powershell).
- High Performance: Built with C++20 coroutines, Boost.Beast, and Boost.Asio, Mojo utilizes a thread-pool architecture with async I/O to maximize throughput, significantly outperforming Python-based crawlers in high-volume tasks due to C++ native performance.
- RAG-Ready Data Ingestion: Automatically transforms noisy HTML into clean, token-efficient Markdown. Perfect for populating vector databases (Pinecone, Milvus, Weaviate) or providing context for LLMs (NotebookLM, Claude, Qwen, etc).
- Proxies:
- Protocol Support: Rotates between SOCKS4, SOCKS5, and HTTP proxies.
- Auto Pruning: Automatically detects and prunes dead or rate-limited proxies (403/429 errors) from the pool.
- Priority Selection: Automatically prioritizes SOCKS5 proxies for improved performance.
- JavaScript Rendering (slower):
- Full Browser Simulation: Uses a headless Chromium instance to execute JavaScript and render dynamic content (SPAs, React, Vue, etc.).
- Magic Proxy Rotation: Bypasses Chromium's static proxy limitation using an internal Reverse Proxy Gateway. This allows the browser to rotate IPs per-request without the heavy overhead of restarting the browser process. This makes it orders of magnitude faster than traditional scrapers (Selenium/Puppeteer) which force a full browser reboot (~1-2s overhead) to switch proxies.
- Stealth Mode: Leverages native Chromium with minimal flags for maximum invisibility.
- Performance: While slower than raw HTTP crawling, it ensures 100% fidelity for dynamic sites.
graph TD
subgraph "Typical (Selenium/Puppeteer)"
A[Start] --> B["Launch Browser <br/> w/ Proxy A"]
B --> C[Visit Page 1]
C --> D[Kill Browser]
D --> E["Launch Browser <br/> w/ Proxy B"]
E --> F[Visit Page 2]
end
subgraph "Mojo (Magic Gateway)"
H[Start] --> I["Launch Browser Once <br/> (Proxy = Mojo Localhost)"]
I --> J[Visit Page 1]
J -- "Traffic" --> K{"Mojo Gateway (Proxy Pool Rotation)"}
K -- "Auto-Rotate" --> L[External Proxy A]
I --> M[Visit Page 2]
M -- "Traffic" --> K
K -- "Auto-Rotate" --> N[External Proxy B]
end
%% Force subgraphs to be one below the other
F ~~~ H
Why is this better?
- Zero Restart Overhead: Traditional tools must kill and restart the entire Chrome process (1-2s delay) just to change an IP. Mojo keeps the browser open and rotates the connection internally.
- Microsecond Switching: Mojo switches the upstream proxy at the TCP socket layer instantly for every request.
- Lower CPU Usage: Avoiding constant browser reboots saves massive amounts of CPU, allowing you to run more concurrent workers.
Mojo operates with two distinct types of threads to ensure maximum throughput:
| Thread Type | Configuration | Responsibility |
|---|---|---|
| Scraping Workers | -t, --threads |
The Decision Makers: Managing the URL queue, visiting pages, extracting links, and saving results. Scaling this visits more pages simultaneously. |
| Gateway Workers | --proxy-threads |
The Couriers: Handling the high-volume background traffic (JS, CSS, images) requested by the browser. Scaling this ensures the browser never stalls. |
The Hierarchy:
If you set -t 8, Mojo visits 8 pages simultaneously. However, a single web page can trigger 50+ network requests. The Gateway Workers ensure those 50+ requests flow smoothly through your proxy rotation without bottlenecking the main scraping agents.
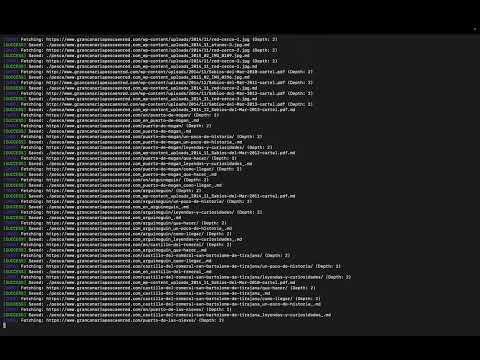
Check out Mojo in action:
Crawl a documentation site to depth 2 and save it as structured Markdown.
./mojo -d 2 https://docs.example.comRender dynamic content using a headless browser.
Note: This mode is slower than standard crawling as it launches a full Chromium instance to execute JavaScript. Use this for SPAs (Single Page Applications) or sites that require JS to display content.
./mojo --render https://spa-example.comCrawl a blog and save all articles into a single directory for easy embedding.
./mojo -d 3 -o ./dataset_raw --flat https://techblog.example.comMojo respects the Robots Exclusion Protocol. To block Mojo from crawling your site, add the following to your robots.txt:
User-agent: Mojo-Crawler/1.0
Disallow: /Or to block all crawlers:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /Notice: Always scrape responsibly. Use proxies properly, follow
robots.txt, respect rate limits, and comply with site terms. If not, Mojo is not the correct fit for you.
Many websites implement IP bans, or geo-restrictions to prevent automated access. By using proxies, Mojo can distribute requests across multiple IP addresses, reducing the risk of blocks and ensuring more reliable crawling.
Important: This feature is intended to help you scrape responsibly, not to bypass site rules. Always follow robots.txt, respect rate limits, and comply with each site's terms of service.
Single proxy with custom gateway threads:
./mojo -p socks5://127.0.0.1:9050 --proxy-threads 64 https://example.comProxy List file:
./mojo --proxy-list proxies.txt https://target-site.comYou can define all settings in a YAML file for cleaner usage.
Run with config:
./mojo --config example_config.yaml https://example.comExample proxies.txt format:
socks5://user:pass@10.0.0.1:1080
http://192.168.1.50:8080
socks4://172.16.0.10:1080
Inside the engine, Mojo manages proxies using a Priority Selection Vector, which favors specific protocols while ensuring high concurrency without resource locking:
- Concurrency: Proxies are shared across all worker threads. The Proxy Gateway uses a configurable Thread Pool (
--proxy-threads) to handle multiple simultaneous requests from the browser efficiently. - Selection: A Round-Robin strategy is used within each priority level to distribute load evenly across healthy proxies.
- Auto-Pruning: Proxies that exceed the retry limit are automatically removed from the rotation.
Priorities:
- SOCKS5 (Priority 2): Highest priority. Faster and more anonymous.
- SOCKS4 (Priority 1): Medium priority.
- HTTP/HTTPS (Priority 0): Lowest priority.
- C++20 Compiler (GCC 12+, Clang 14+, or MSVC 2022+)
- CMake 3.10+
- Boost (Asio, Beast, System)
- libgumbo (HTML Parsing)
- libwebsockets (WebSocket Communication)
- yaml-cpp (YAML Parsing)
- CLI11 (Command Line Parser)
- nlohmann_json (JSON Parsing)
- Google Chrome is required at runtime for JS rendering.
- Abseil (Google Common Libraries)
1. Install Dependencies:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install build-essential cmake git libcurl4-openssl-dev libgumbo-dev libwebsockets-dev libyaml-cpp-dev libcli11-dev nlohmann-json3-dev libcap-dev libuv1-dev libev-dev zlib1g-dev libabsl-dev2. Build & Package (DEB):
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DMOJO_STATIC_BUILD=ON
make -j$(nproc)
# Create .deb package
cpack -G DEBOutput: mojo-0.1.0-Linux.deb
3. Install Package:
sudo dpkg -i mojo-*.deb1. Install Dependencies:
sudo dnf install git cmake make gcc-c++ libcurl-devel gumbo-parser-devel libwebsockets-devel nlohmann-json-devel yaml-cpp-devel cli11-devel libcap-devel libuv-devel libev-devel zlib-devel abseil-cpp-devel rpm-build2. Build & Package (RPM):
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DMOJO_STATIC_BUILD=ON
make -j$(nproc)
# Create .rpm package
cpack -G RPMOutput: mojo-0.1.0-Linux.rpm
3. Install Package:
sudo rpm -i mojo-*.rpm1. Install Dependencies (Homebrew):
brew install cmake curl gumbo-parser libwebsockets nlohmann-json yaml-cpp cli11 abseil2. Build:
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release
make -j$(sysctl -n hw.ncpu)3. Package & Install:
# To verify functionality
./mojo --help
# To install system-wide
sudo cp mojo /usr/local/bin/
# To create a distributable zip
zip mojo-macos.zip mojo1. Install Dependencies (vcpkg):
Assuming you have vcpkg installed at C:\vcpkg:
vcpkg install curl gumbo nlohmann-json libwebsockets yaml-cpp cli11 libuv zlib abseil --triplet x64-windows-static
vcpkg integrate install2. Build:
mkdir build; cd build
cmake .. -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DVCPKG_TARGET_TRIPLET=x64-windows-static -DCMAKE_TOOLCHAIN_FILE="C:/vcpkg/scripts/buildsystems/vcpkg.cmake"
cmake --build . --config Release3. Package & Install:
The executable is located at Release\mojo.exe.
- Install: Add the
Releasefolder to your system PATH. - Package: Right-click
mojo.exe-> Send to -> Compressed (zipped) folder.
Mojo is released under the MIT License.
This project incorporates the google/robotstxt library, which is licensed under the Apache License 2.0.
See src/utils/robotstxt/LICENSE for more details.