Website | Documentation | Changelog server | Changelog testrunner | Bluesky | Mastodon
Setup your own online version of sitespeed.io. You get:
-
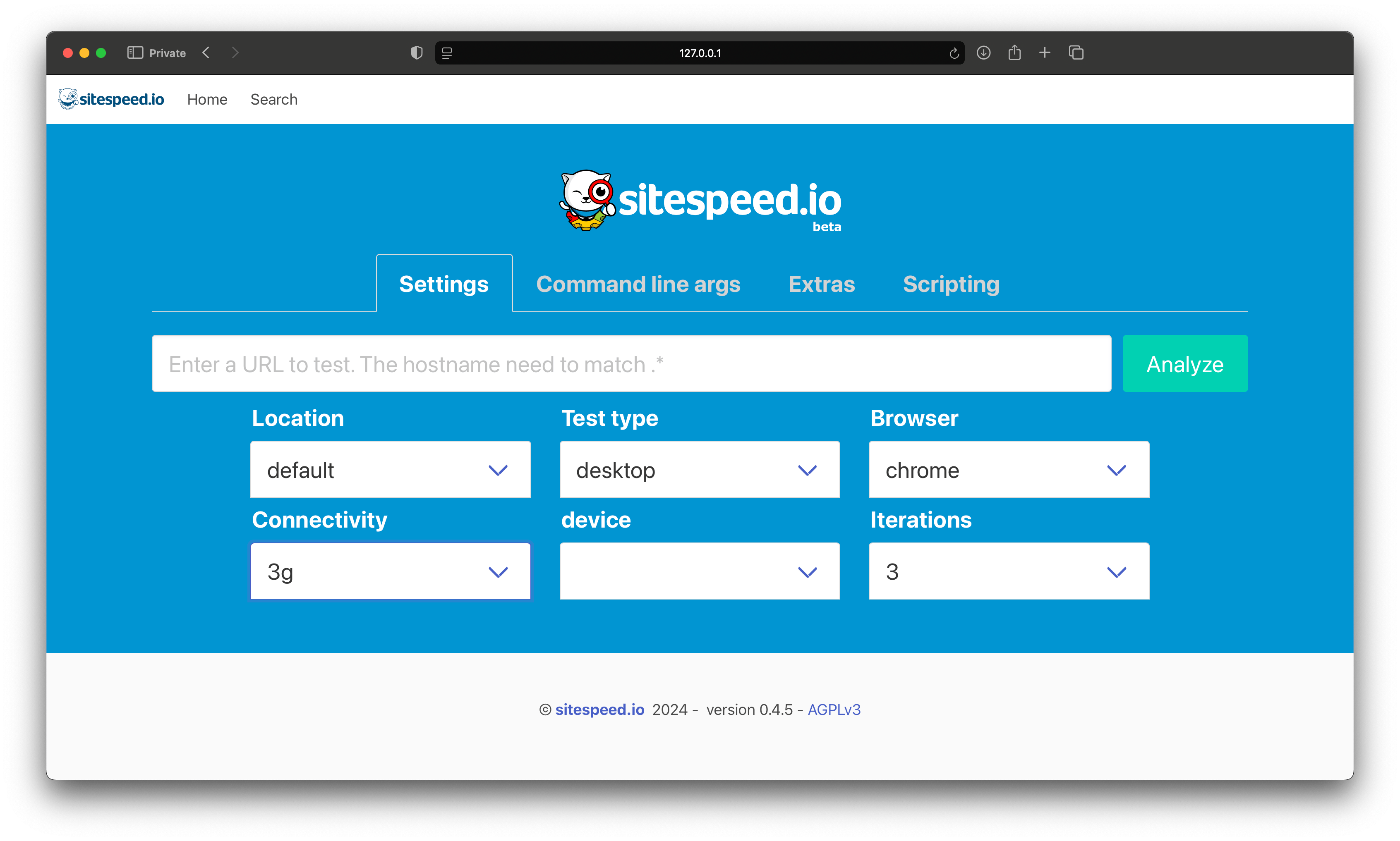
A server with GUI and API:
- Add tests using a HTML frontend (you can style the frontend using your own CSS)
- Add tests using the command line (using
sitespeed.io --api.hostname my.host.com --api.location default https://www.sitespeed.io)
- Add tests using a HTML frontend (you can style the frontend using your own CSS)
-
Test Runners:
- Run your tests on different platforms: desktop, emulated mobile and Android.
-
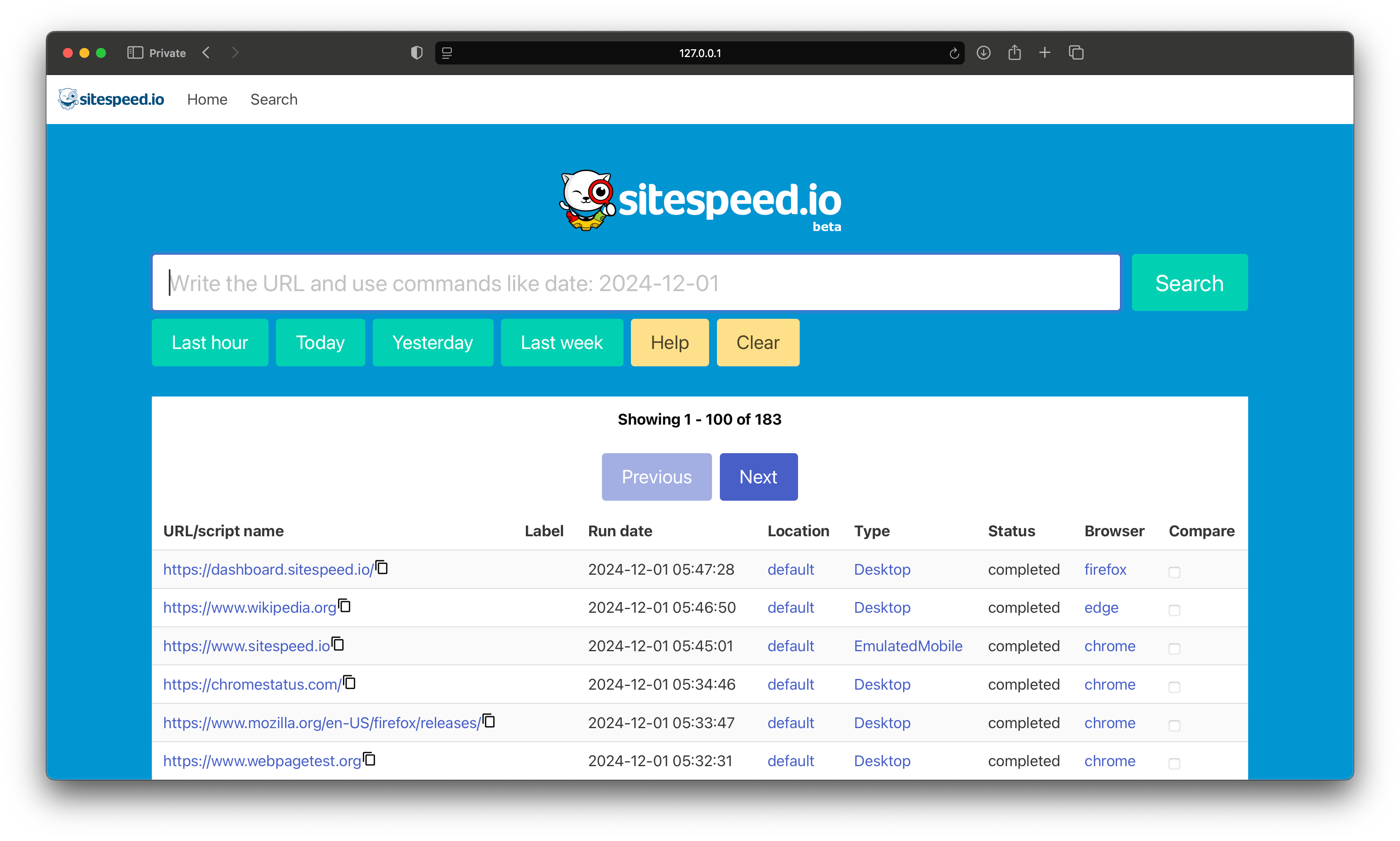
Search Functionality:
Follow these steps to quickly set up and run the online version of sitespeed.io on your local Linux or Mac OS machine. Make sure you have Docker and docker compose installed. The default Docker compose setup use the same Docker network and have only the ports open that is needed.
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/sitespeedio/onlinetest.git
-
Navigate to the project directory:
cd onlinetest -
Copy the example environment file:
cp .env.example .env
-
Start the Docker containers (Redis/PostgreSQL/Minio/sitespeed.io server and testrunner) on the same server:
docker compose -f docker-compose.dependencies.yml -f docker-compose.server.yml -f docker-compose.testrunner.yml up
Now you can open your web browser and navigate to http://127.0.0.1:3000 to run your first test.
If you are on Linux you need to run sudo modprobe ifb numifbs=1 to be able to set different connectivites inside of Docker. On Mac you can only run native connectivity when you run inside of Docker.
To deploy on a server you should check the production setup.
The .env.example has the configuration that you usually needs to change/configure between different environment. If you use the .env file, it will automatically be picked up.
You can configure everything that you are used to configure with sitespeed.io + more. The server and the testrunner takes --config /path/to/file.
There's a regular expression that validates the domain of the URL that you want to test. You can use this to make sure a public instance only can tests pages on your web sites.
VALID_TEST_DOMAINS=".*"
By default latest major release of sitespeed.io is configured, it looks like this in the .env file:
SITESPEED_IO_CONTAINER="sitespeedio/sitespeed.io:39"
When 40 is released you just switch to:
SITESPEED_IO_CONTAINER="sitespeedio/sitespeed.io:40"
To get latest version of 35 you need to periodically pull down the version:
docker pull sitespeedio/sitespeed.io:35
If you want to run a specific version, you can pin the version to a specific version:
SITESPEED_IO_CONTAINER="sitespeedio/sitespeed.io:39.0.0"
Running on your own machine the result is served from localhost. If you deploy on a server you want to change that:
RESULT_BASE_URL="http://127.0.0.1:9000/sitespeedio"
By default the result is served by MinIO on port 9000. If you serve the result on the URL https://sitespeed.domain.com you change your result base to: RESULT_BASE_URL="https://sitespeed.domain.com/sitespeedio"
You can configure which version of the server and the testrunner you want to use. You can either use latest stable version or specify a specific tag. In the .env file you configure which Docker tag to use.
SITESPEED_IO_SERVER_VERSION=1
SITESPEED_IO_TESTRUNNER_VERSION=1
If you do not want to use Docker for the server and the testrunner you can use NodeJS libraries directly. Install the testrunner and the server:
npm install @sitespeed.io/server -g
npm install @sitespeed.io/testrunner -gYou then need the depencencies (PostgreSQL/Redis etc) and the easiet way to get them running is to use the docker compose file:
git clone https://github.com/sitespeedio/onlinetest.git
cd onlinetest
docker compose -f docker-compose.dependencies.yml -f standalone/docker-compose.dependencies.standalone.yml -f -dThen start the testrunner and the server:
sitespeed.io-testrunner
sitespeed.io-serverIn the real world you want to also supply your own configuration files. Default server configuration and testrunner configuration:
sitespeed.io-testrunner --config path/to/testrunnerfile
sitespeed.io-server --config path/to/fileTo get it up and running (the docker-compose file), you need:
-
A Message broker: - A Redis-like data storage/message broker. The default setup uses Redis and has also been tested with Valkey.
-
A Database: - PostgreSQL - the open source database.
-
A Test Result Storage: - Somewhere to store test results. The default setup uses minio, an open source implementation of S3 but you can use all the result storages that work with sitespeed.io: S3, Google Cloud Storage or your own storage where you can scp the result.
Additionally, there's a server and one or multiple test runners that run the sitespeed.io tests.
Production means work. You can read more about it at deployments.
Running servers and testing costs money and you can help support sitespeed.io at Open Collective.